Ischemic Heart Disease is a condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle due to narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, which are the blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart. This reduced blood flow can lead to chest pain, also known as angina, or in more severe cases, a heart attack, which occurs when a portion of the heart muscle is damaged or dies due to lack of blood supply.
The most common cause of IHD is atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up inside the walls of the coronary arteries, causing them to narrow and harden over time. Other risk factors for IHD include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a family history of heart disease.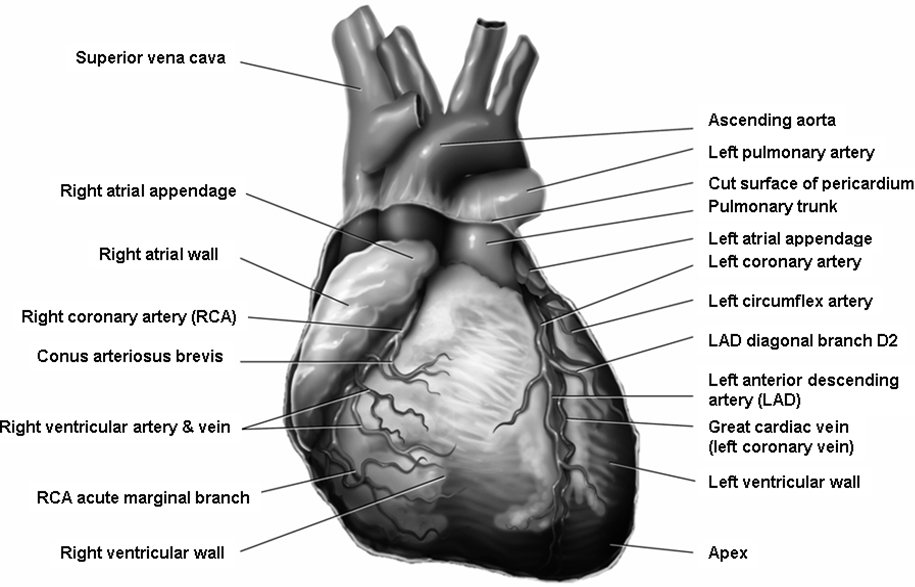
Treatment for IHD may include lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and following a heart-healthy diet, as well as medications such as aspirin, beta-blockers, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart. Prevention of IHD involves managing the risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle.

