Myasthenia gravis is a rare neuromuscular disorder that affects the muscles responsible for voluntary movement. The condition is characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue, which can range from mild to severe. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of myasthenia gravis can vary widely between individuals. However, the most common symptom is muscle weakness, which typically affects the eyes, face, throat, and limbs. Some of the other common symptoms include:
- Difficulty speaking, chewing, and swallowing
- Drooping eyelids
- Double vision
- Weakness in the arms and legs
- Breathing difficulties
The symptoms of myasthenia gravis tend to worsen with activity and improve with rest. Therefore, people with myasthenia gravis often experience muscle fatigue and weakness towards the end of the day or after prolonged activity.
Diagnosis:
The diagnosis of myasthenia gravis is based on a combination of clinical evaluation, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The doctor will take a detailed medical history and perform a physical examination to look for signs of muscle weakness and fatigue.
Some of the laboratory tests used to diagnose myasthenia gravis include:
- Edrophonium test: This test involves injecting a medication called Edrophonium, which temporarily improves muscle strength in people with myasthenia gravis.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can detect the presence of antibodies that attack the receptors responsible for muscle contraction.
- Electromyography (EMG): This test measures the electrical activity of the muscles and can help determine the extent of muscle weakness.
Treatment:
The treatment of myasthenia gravis involves a combination of medications, surgery, and lifestyle modifications. The aim of treatment is to improve muscle strength, reduce symptoms, and prevent complications.
Medications:
There are several medications used to treat myasthenia gravis, including:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors: These drugs improve muscle strength by preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is important for muscle contraction.
- Immunosuppressants: These drugs reduce the activity of the immune system, which can help prevent the production of antibodies that attack the muscles.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG): This treatment involves infusing a solution of antibodies derived from healthy donors, which can help reduce the activity of the antibodies that attack the muscles.
Surgery:
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat myasthenia gravis. The most common surgical procedure is thymectomy, which involves removing the thymus gland. The thymus gland is thought to play a role in the production of the antibodies that attack the muscles, so removing it can help reduce the activity of these antibodies.
Lifestyle modifications:
There are several lifestyle modifications that can help improve the symptoms of myasthenia gravis, including:
- Rest: People with myasthenia gravis should avoid prolonged activity and take regular breaks to rest.
- Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet can help provide the nutrients needed for muscle function.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help improve muscle strength and reduce fatigue.
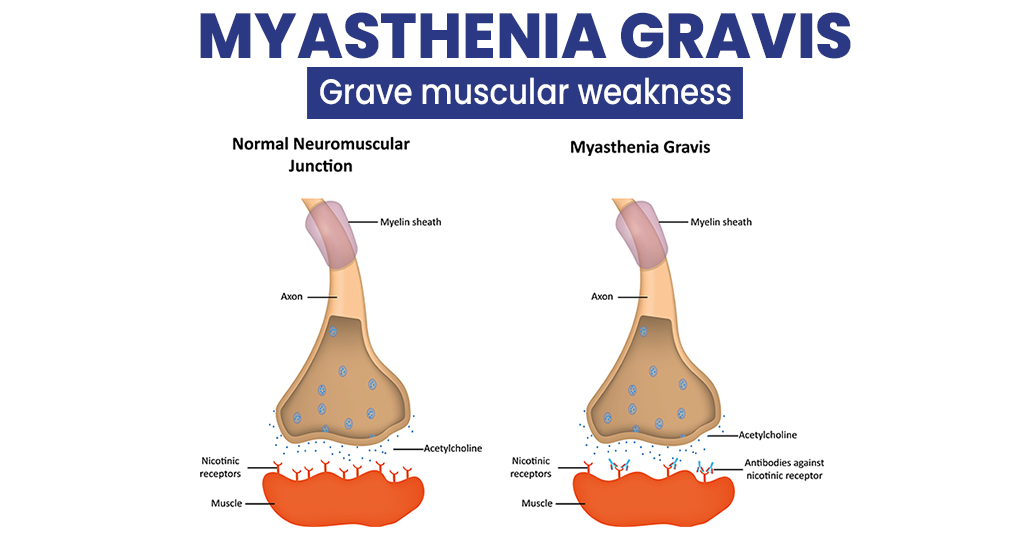
myasthenia gravis is a rare neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. The condition can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes, face, throat, and limbs. The diagnosis of myasthenia gravis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The treatment of myasthenia gravis involves a combination of medications, surgery, and lifestyle modifications, aimed at improving muscle strength, reducing symptoms, and preventing complications.

