A brain tumour is a mass or growth of abnormal cells that develop within the brain. This growth can be either cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). While some brain tumours are benign and can be easily treated, others can be life-threatening and require urgent medical attention. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of brain tumours.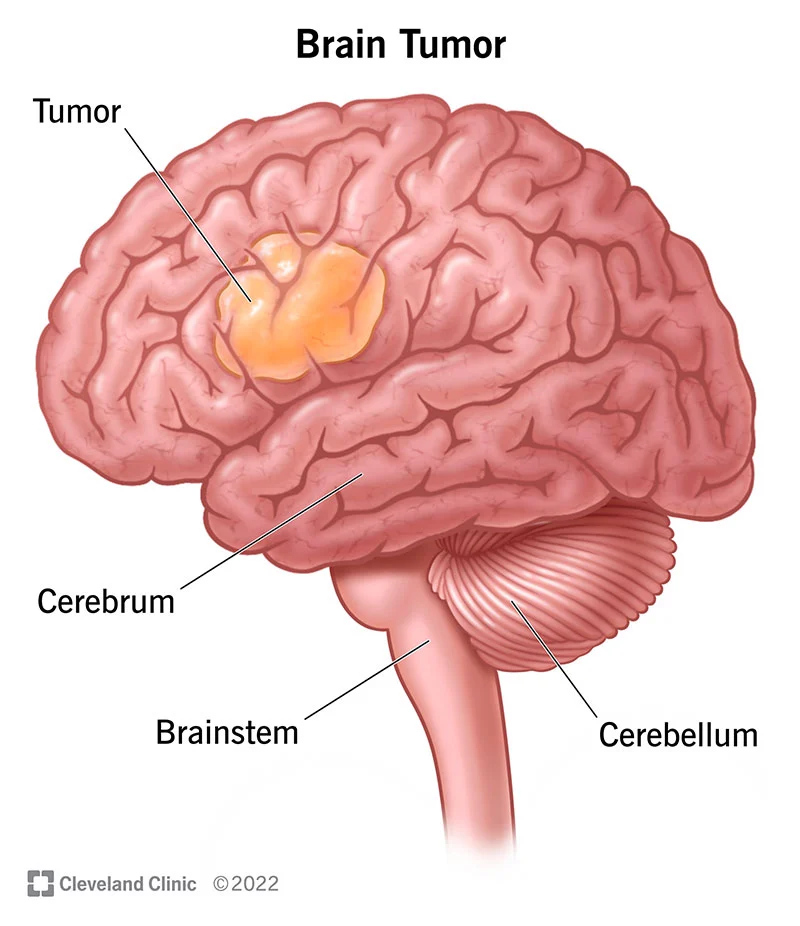
Causes: The exact cause of brain tumours is unknown, but certain risk factors are known to increase the chances of developing a brain tumour. These include exposure to ionizing radiation, a family history of brain tumours, a weakened immune system, and certain genetic syndromes. It is important to note, however, that not all brain tumours are caused by these factors.
Symptoms: The symptoms of a brain tumour can vary depending on the size, location, and type of tumour. Some common symptoms include headaches, seizures, weakness or numbness in the arms or legs, balance problems, changes in vision or hearing, and difficulty speaking or understanding language. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Diagnosis: If a doctor suspects a brain tumour, they will likely perform a series of tests to make a definitive diagnosis. These tests may include imaging tests such as CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans, as well as a biopsy, in which a small sample of tissue is removed and examined for cancerous cells. A neurologist will typically perform these tests and interpret the results to determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment: The treatment for a brain tumour will depend on the size, location, and type of tumour, as well as the overall health of the patient. For benign tumours, a doctor may recommend monitoring the tumour with regular imaging tests and only treating it if it begins to grow. If the tumour is cancerous, however, the doctor will likely recommend surgery to remove as much of the tumour as possible, followed by radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy to kill any remaining cancer cells. In some cases, a combination of these treatments may be recommended.
Living with a Brain Tumour: Living with a brain tumour can be challenging, but there are resources available to help. Support groups, for example, can provide a sense of community and connection for those living with a brain tumour. Rehabilitation services, such as physical therapy or speech therapy, can also help patients regain function after surgery or other treatments. It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques.
A brain tumour is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of a brain tumour, it is important to see a doctor right away. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many brain tumours can be successfully treated, allowing patients to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.

