Symptoms and Treatment.
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition that causes pain, pressure, and discomfort in the pelvic area. It affects an estimated 3 to 8 million people in the United States, and it can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. In this article, we will explore the symptoms and treatment options for interstitial cystitis.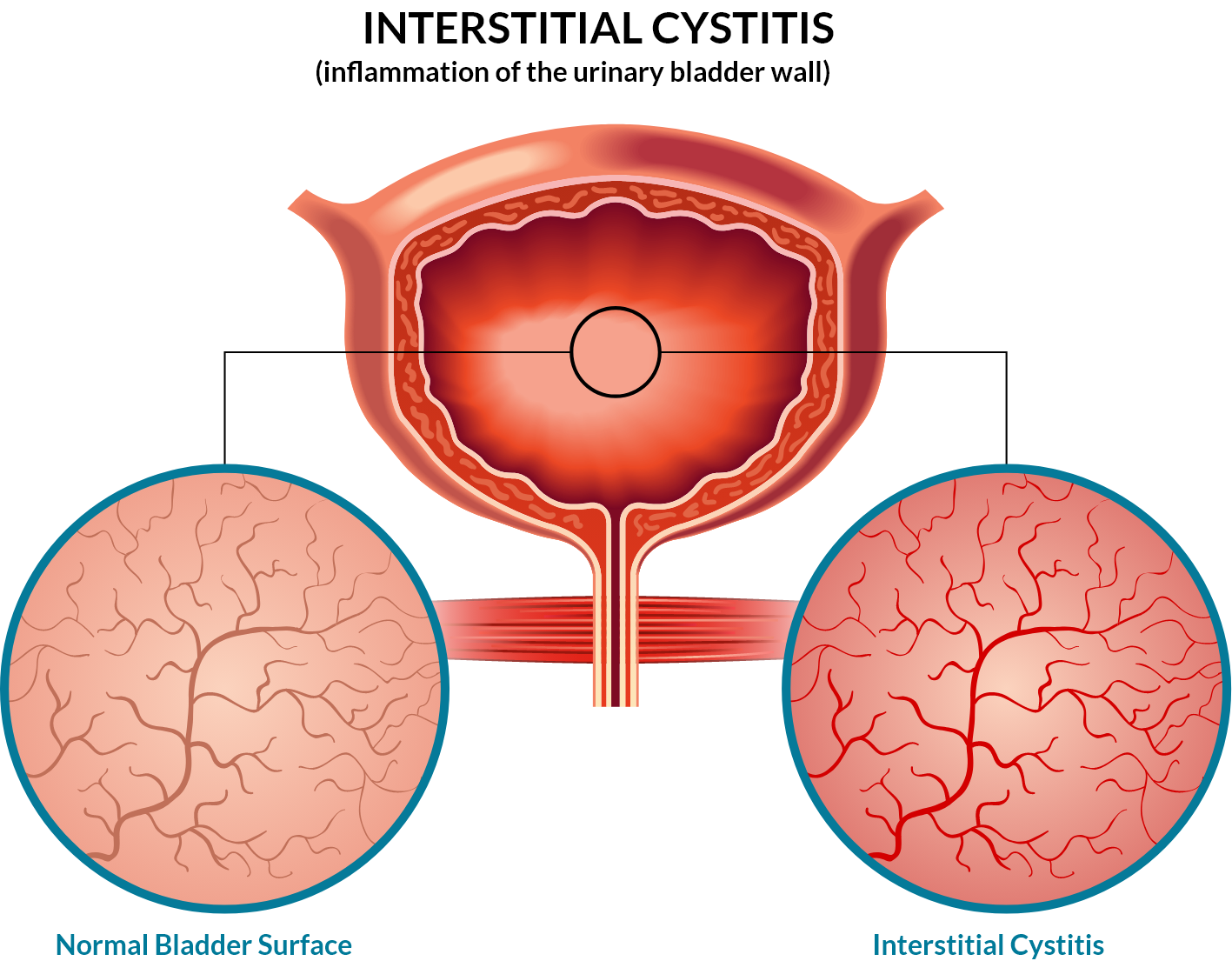
Symptoms of Interstitial Cystitis:
The symptoms of interstitial cystitis can vary from person to person, but they typically involve chronic pain or discomfort in the pelvic region. Some of the most common symptoms of interstitial cystitis include:
- Frequent urination: Individuals with interstitial cystitis may feel the need to urinate frequently, even when their bladder is not full. They may also experience urinary urgency, which is a sudden and intense urge to urinate.
- Painful urination: Individuals with interstitial cystitis may experience pain or discomfort during urination.
- Pelvic pain: Interstitial cystitis can cause chronic pain or discomfort in the pelvic area. This pain may be dull or sharp and may worsen during periods of stress.
- Pain during intercourse: Interstitial cystitis can also cause pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse.
- Incontinence: In some cases, interstitial cystitis may lead to urinary incontinence, which is the involuntary leakage of urine.

Treatment Options for Interstitial Cystitis:
There is no known cure for interstitial cystitis, but there are several treatment options available to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Some of the most common treatment options for interstitial cystitis include:
- Bladder instillation: This is a procedure in which medication is inserted into the bladder through a catheter. The medication is left in the bladder for a short period of time before being drained out.
- Oral medications: Certain medications, such as antihistamines and antidepressants, can help relieve the symptoms of interstitial cystitis.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control.
- Dietary changes: Certain foods and beverages, such as spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol, can exacerbate the symptoms of interstitial cystitis. Making dietary changes can help reduce symptoms.
- Nerve stimulation: Nerve stimulation can help relieve pain and improve bladder function in individuals with interstitial cystitis.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to remove the bladder or to implant a device that stimulates the nerves in the bladder.

Living with Interstitial Cystitis:
Living with interstitial cystitis can be challenging, but there are several things that individuals with this condition can do to improve their quality of life. Some of the most important things to keep in mind include:
- Practice stress management: Stress can exacerbate the symptoms of interstitial cystitis. Finding ways to manage stress, such as through meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help reduce symptoms.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help flush out the bladder and reduce symptoms.
- Avoid triggers: Certain foods and beverages, such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, can exacerbate the symptoms of interstitial cystitis. Avoiding these triggers can help reduce symptoms.
- Use pelvic floor exercises: Pelvic floor exercises can help strengthen the muscles that control the bladder and improve bladder control.
- Talk to a healthcare provider: If you are experiencing symptoms of interstitial cystitis, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider. They can help determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation.
Cystitis is a chronic bladder condition that can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. While there is no known cure for this condition, there are several treatment options available to help.