Obsessive-compulsive disorder, or OCD, is a mental health condition characterized by unwanted, intrusive, and often disturbing thoughts or obsessions, that lead to repetitive behaviors or compulsions. The symptoms of OCD can be distressing and disruptive to one’s life, but with proper treatment, most people with OCD can manage their symptoms and live a full and productive life.
In this blog post, we will explore what OCD is, the symptoms, causes, and available treatments.
What is OCD?
OCD is a type of anxiety disorder that affects about 1-2% of the population. It involves experiencing recurring and intrusive thoughts, images, or impulses that are distressing, and which one tries to ignore, suppress or neutralize through compulsive or ritualistic behaviors.
The compulsions or rituals are often time-consuming, distressing, and interfere with daily activities, relationships, and productivity. Individuals with OCD may recognize that their obsessions and compulsions are irrational, yet find it challenging to stop or control them.
Symptoms of OCD
The symptoms of OCD vary from one person to another and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include:
- Compulsive or ritualistic behaviors that are repetitive, time-consuming, and often done to reduce anxiety or prevent harm, such as excessive cleaning, checking, counting, repeating words or phrases, or arranging things in a specific order.
- Avoidance behaviors, where individuals avoid certain situations or people to prevent triggering obsessions or compulsions.
- Emotional distress, including anxiety, fear, guilt, and shame, and the need for reassurance from others.
- Interference with daily activities, relationships, and productivity.

Causes of OCD
The causes of OCD are not entirely understood, but research suggests that it involves a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurobiological factors.
Genetic factors: Studies have shown that OCD tends to run in families, and some genes may increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Environmental factors: Trauma, abuse, neglect, or significant life changes, such as childbirth or bereavement, may trigger or exacerbate OCD symptoms.
Neurobiological factors: There is evidence to suggest that imbalances in brain chemistry and activity in certain areas of the brain, such as the basal ganglia and the frontal cortex, may contribute to the development of OCD.
Available Treatments for OCD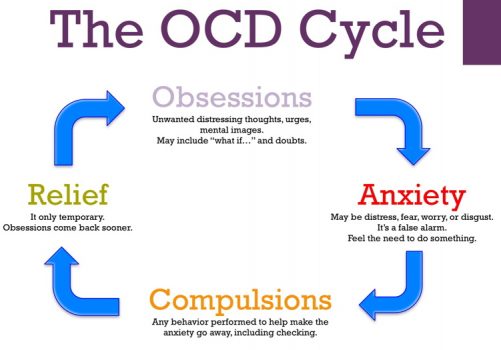
OCD is a treatable condition, and several treatment options are available, including medication, psychotherapy, and self-help strategies.
Medication: Antidepressant medications, particularly selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are commonly used to treat OCD. These drugs work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and anxiety. Other medications, such as antipsychotics, may be used in severe cases or when OCD is resistant to other treatments.
Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is the most effective type of therapy for OCD. It involves exposure and response prevention (ERP), which is a type of therapy that exposes individuals to their feared situations or objects, and helps them to learn healthier ways to respond. ERP has been found to be very effective in reducing OCD symptoms.
Self-help strategies: Individuals with OCD can benefit from several self-help strategies, including mindfulness, relaxation techniques, exercise, and a healthy lifestyle. These can help reduce stress, improve mood, and promote well-being.
Conclusion
OCD is a challenging mental health condition that affects many people worldwide. It involves persistent, intrusive thoughts or obsessions, which lead to repetitive behaviors or compulsions. Although OCD can be distressing
























