Arthritis is a term used to describe a group of conditions that cause inflammation in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the two most common types of arthritis, with osteoarthritis being more prevalent and often referred to as “wear and tear” arthritis.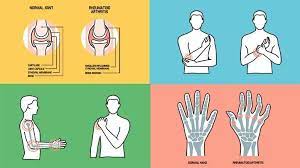
Osteoarthritis:
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints begins to wear down, leading to bone rubbing against bone. This can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion in the affected joint.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis may include joint pain and tenderness, stiffness, a grinding or crunching feeling when moving the joint, and bone spurs (small bony growths) around the joint. Osteoarthritis most commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the hips, knees, and spine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Pain in the hands, wrists, and feet.
Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, obesity, joint injury or overuse, and a family history of the condition. Treatment options for osteoarthritis may include medications to reduce pain and inflammation, physical therapy to improve joint function and flexibility, and lifestyle changes such as weight loss and regular exercise. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be recommended.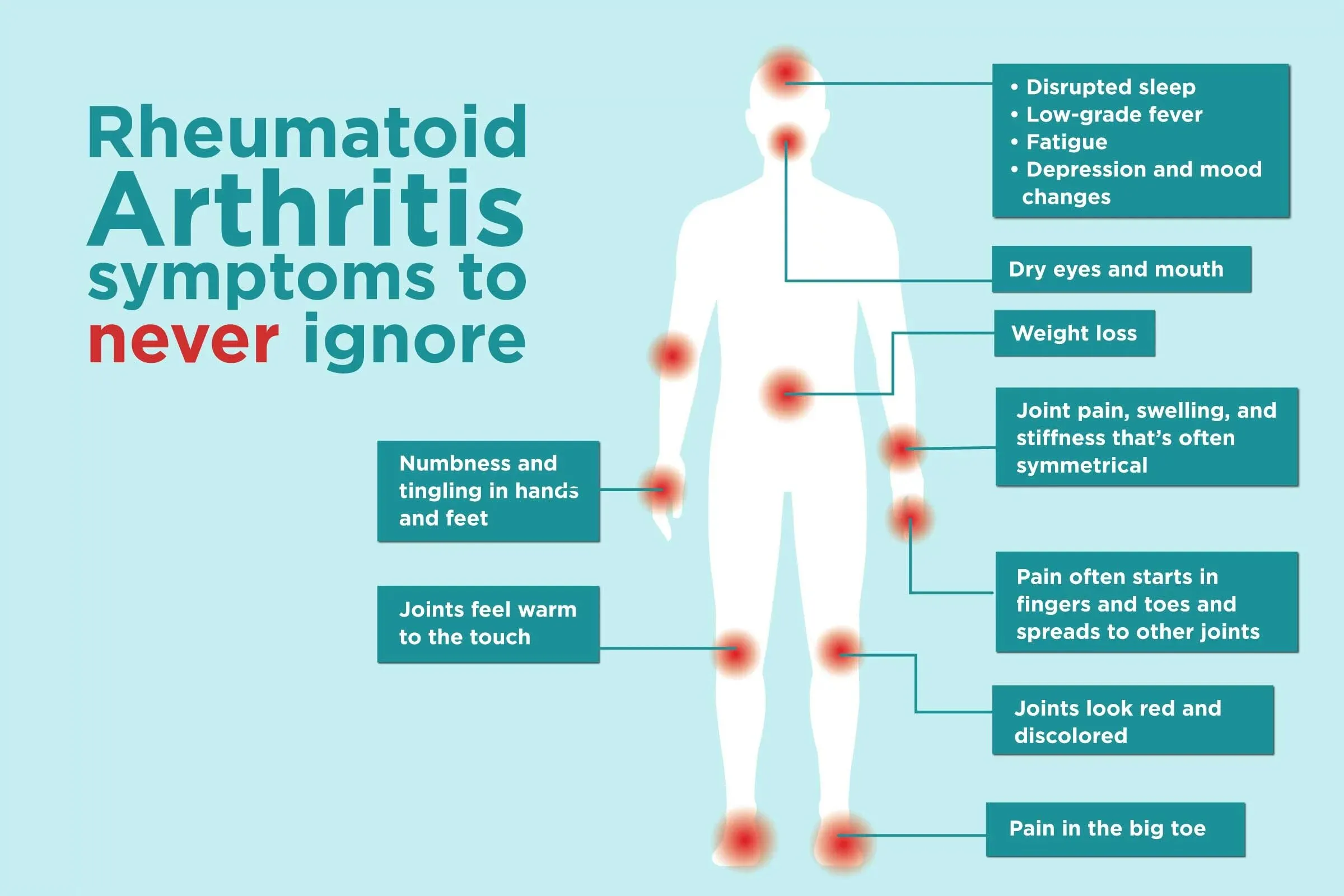
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the joints, leading to inflammation and damage. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is often caused by wear and tear on the joints, rheumatoid arthritis can affect people of all ages and is more common in women than men.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may include joint pain and swelling, stiffness, fatigue, and a general feeling of malaise. The condition can affect any joint in the body, but often begins in the hands and feet.
Treatment options for rheumatoid arthritis may include medications to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease, physical therapy to maintain joint function and improve flexibility, and lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and stress reduction. In some cases, surgery may be recommended to repair or replace damaged joints.
One of the most important things a person with arthritis can do is to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. This may involve a combination of medical and non-medical treatments, such as physical therapy and exercise, weight management, and stress reduction techniques.
In addition to medical treatments, there are a number of self-care strategies that can help manage the symptoms of arthritis. These may include maintaining a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and using hot and cold therapies to reduce pain and inflammation.
Living with arthritis can be challenging, but with the right treatment plan and support, people with the condition can maintain a good quality of life. It is important to stay informed about the latest advances in arthritis treatment and to work closely with a healthcare provider to manage the condition effectively.