Periodontal gum disease is a serious condition that affects the that support your teeth. The disease causes inflammation and can lead to the destruction of your teeth and gums, eventually resulting in tooth loss. The condition is caused by bacteria that live in plaque and tartar, which can build up on teeth over time. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms of periodontal gum disease and the various treatments available.
Symptoms of Periodontal Gum Disease
Periodontal gum disease is a progressive condition, and the symptoms may not be noticeable until the later stages of the disease. However, there are some common symptoms to look out for. These include:
- Gum bleeding: This is the most common symptom of periodontal gum disease. If your gums bleed when you brush or floss, it is an indication of inflammation caused by the bacteria.
- Swollen or red gums: If your gums are swollen or red, it is an indication that your body is fighting off an infection caused by the bacteria.
- Bad breath: If you have bad breath that does not go away after brushing, it could be a sign of periodontal gum disease.
- Loose or shifting teeth: As the bacteria destroy the tissues supporting your teeth, your teeth may start to shift or feel loose.
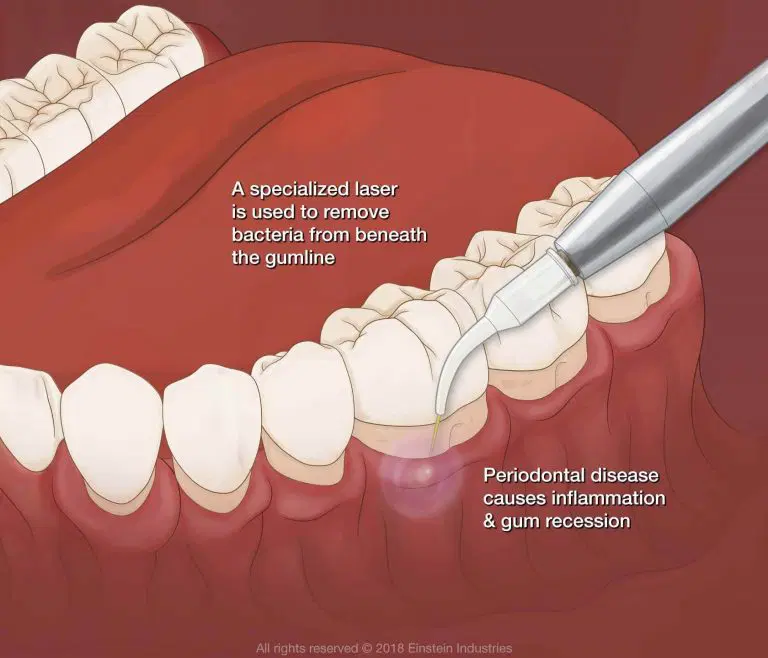
- Receding gums: As the disease progresses, the gum tissue may start to pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth.

The treatment of periodontal gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. There are several treatment options available, including:
- Scaling and root planning: This is a non-surgical treatment that involves cleaning the teeth to remove plaque and tartar. It also involves smoothing out the root surfaces to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the bacteria that are causing the infection.
- Surgery: If the disease has progressed to a severe stage, surgery may be required to remove damaged tissue and reposition the gums.
- Gum grafts: If the gums have receded, gum grafts can be performed to help protect the roots of the teeth and reduce sensitivity.
- Dental implants: If you have lost teeth as a result of periodontal gum disease, dental implants may be an option to replace the missing teeth.
Preventing Periodontal Gum Disease
Preventing periodontal gum disease is the best way to avoid the pain and expense of treatment. Here are some tips for preventing periodontal gum disease:
- Brush and floss regularly: Brushing and flossing help remove the bacteria that cause gum disease.
- Use mouthwash: Mouthwash can help kill bacteria that brushing and flossing may have missed.
- Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet can help boost your immune system, which can help fight off infections.
- Avoid smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for periodontal gum disease.
- Visit your dentist regularly: Regular dental visits can help detect early signs of gum disease and prevent the disease from progressing.
Periodontal gum disease is a serious condition that requires early detection and treatment to prevent tooth loss. If you are experiencing any symptoms of gum disease, it is important to see your dentist as soon as possible. Your dentist can recommend the appropriate treatment for your condition and provide advice on how to prevent the disease from returning. By taking care of your teeth and gums, you can prevent periodontal gum disease and enjoy a healthy smile for years to come.




