Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, is a common dental problem that occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acid that erodes the enamel of the teeth. This condition is prevalent in all age groups and is the leading cause of tooth loss in children and adults.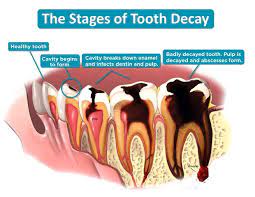
Symptoms of Tooth Decay: Tooth decay can be difficult to detect in its early stages, which is why regular dental checkups are essential. However, there are some symptoms to watch out for that may indicate the presence of tooth decay. These include:
- Tooth sensitivity to hot or cold foods or drinks
- Pain when chewing
- Visible holes or pits in the teeth
- Discoloration of the teeth, often appearing as brown or black spots
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
If left untreated, tooth decay can progress and lead to more severe symptoms, such as severe pain, abscesses, and even tooth loss.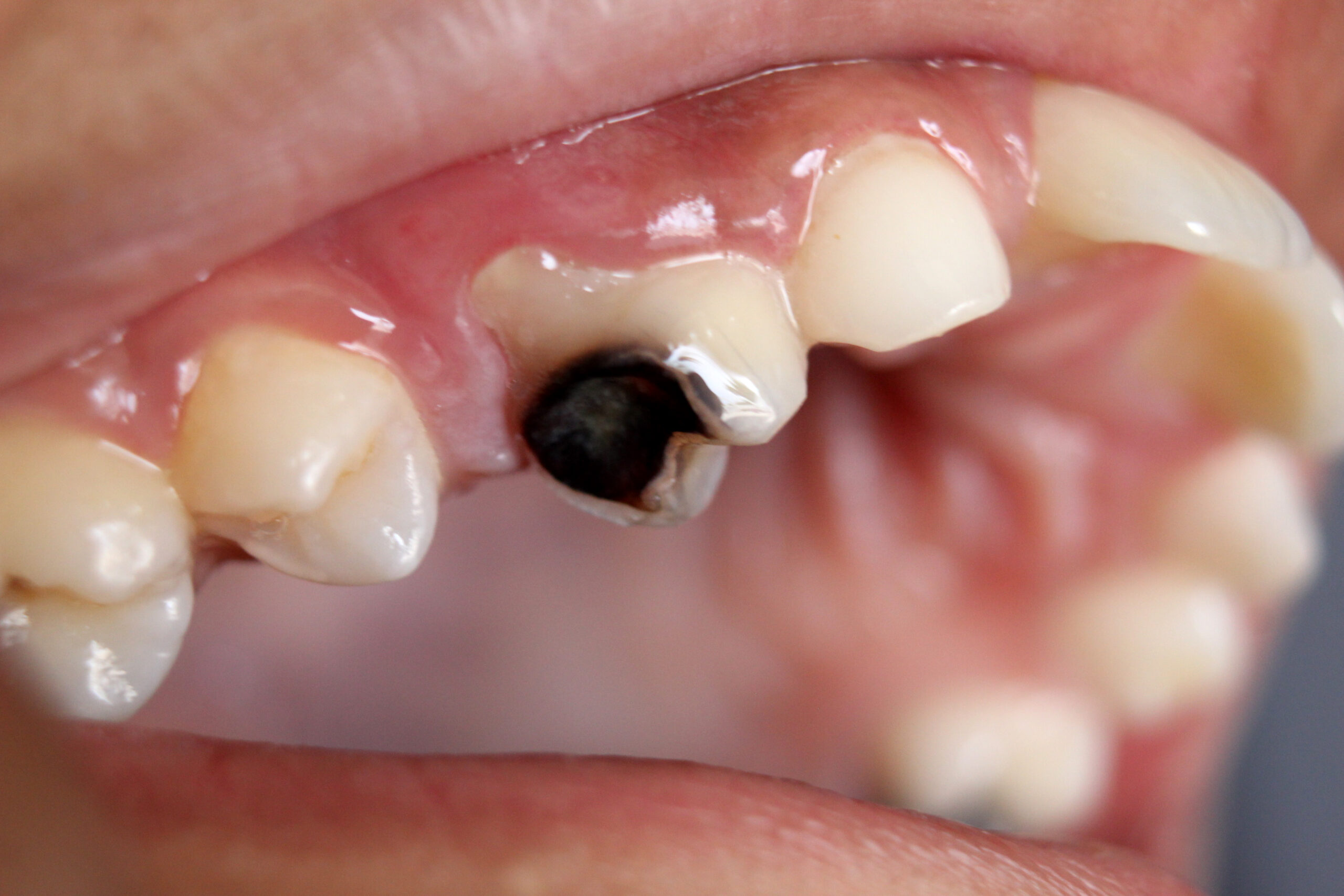
Treatment of Tooth Decay: The treatment for tooth decay depends on the severity of the decay. If detected in the early stages, the decay can often be reversed or slowed down through a combination of good oral hygiene practices and professional dental care.
- Fluoride Treatment: Professional fluoride treatment is a common method used to slow down the progression of tooth decay. Fluoride is a mineral that helps to strengthen the tooth enamel and can even reverse early stages of decay.
- Dental Fillings: If the decay has progressed beyond the early stages, a dental filling may be required to restore the tooth. A filling involves removing the decayed portion of the tooth and filling the space with a tooth-colored material such as composite resin, amalgam, or gold.
- Root Canal Treatment: If the decay has reached the pulp of the tooth, a root canal treatment may be necessary. This involves removing the infected or inflamed pulp from the tooth and filling the space with a special material.
- Extraction: In some cases, if the tooth decay is too severe or if the tooth is causing pain, extraction may be the only solution. The tooth will be removed, and in some cases, it may be necessary to replace it with a dental implant or bridge.
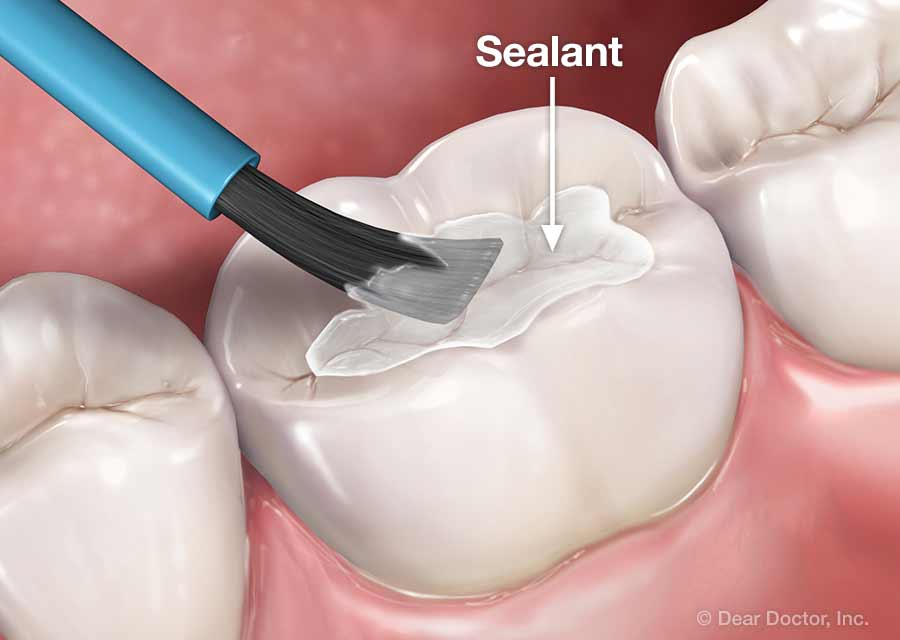
Prevention of Tooth Decay: Preventing tooth decay is always better than treating it. The following are some steps that can be taken to prevent tooth decay:
- Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash can help to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth, reducing the risk of tooth decay.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a well-balanced diet, avoiding sugary foods and drinks, and drinking plenty of water can help to keep the teeth healthy.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Regular dental checkups every six months can help to detect tooth decay in its early stages and prevent it from progressing.
Tooth decay is a common dental problem that can cause a range of symptoms, from tooth sensitivity to severe pain and tooth loss. Treatment options depend on the severity of the decay, and prevention is always better than treatment. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, eating a healthy diet, and visiting the dentist regularly can help to prevent tooth decay and maintain good oral health.

 Individuals with hypersomnolence disorder may experience difficulty staying awake during activities such as work, school, or driving. The disorder can interfere with daily activities and cause significant impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning. The exact causes of hypersomnolence disorder are not well understood, but it may be related to a variety of factors, including genetics, neurological conditions, and psychological factors.
Individuals with hypersomnolence disorder may experience difficulty staying awake during activities such as work, school, or driving. The disorder can interfere with daily activities and cause significant impairment in social, occupational, or other areas of functioning. The exact causes of hypersomnolence disorder are not well understood, but it may be related to a variety of factors, including genetics, neurological conditions, and psychological factors.