Muscular dystrophy is a group of genetic disorders that affect muscle function and structure. It is a progressive disease, meaning it gets worse over time, and can lead to disability and loss of mobility. The symptoms of muscular dystrophy can vary greatly depending on the type of muscular dystrophy and the severity of the disease.
There are several different types of muscular dystrophy, each with its own unique set of symptoms. Some of the most common types include Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Becker muscular dystrophy, limb-girdle muscular dystrophy.
All types of muscular dystrophy are caused by mutations in genes that are responsible for the production of proteins that are essential for healthy muscle function.
One of the most common symptoms of muscular dystrophy is muscle weakness, which can affect the arms, legs, and trunk. This can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as standing up, walking, and even breathing. In some cases, the weakness may be more severe on one side of the body than the other. Other symptoms of muscular dystrophy can include muscle cramps, stiffness, and wasting.
Muscular dystrophy can also cause problems with the heart and lungs. This is because the muscles that control breathing and the muscles that make up the heart are also affected by the disease. As the disease progresses, individuals with muscular dystrophy may require assistance with breathing and may develop heart problems.
Currently, there is no cure for muscular dystrophy. However, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms of the disease and improve quality of life. Physical therapy can help maintain muscle strength and flexibility, while occupational therapy can help individuals learn how to perform everyday tasks in new ways. Braces and other assistive devices may also be helpful in maintaining mobility.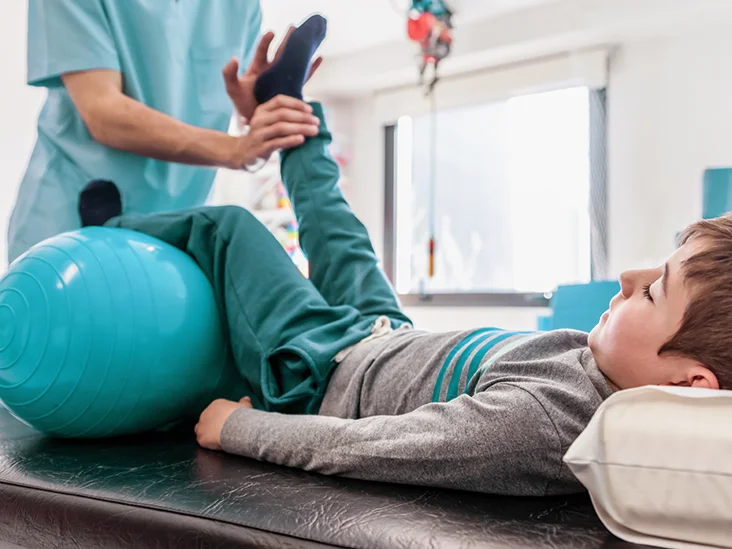
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of muscular dystrophy. For example, corticosteroids may be prescribed to help reduce inflammation in the muscles and improve muscle strength. Other medications may be prescribed to help manage specific symptoms, such as muscle cramps or heart problems.
Research is ongoing to develop new treatments for muscular dystrophy. Some of the most promising research is focused on gene therapy, which involves delivering healthy copies of the faulty genes that cause muscular dystrophy to affected muscles. While gene therapy is still in the experimental stage, it has shown promise in clinical trials and may one day offer a cure for muscular dystrophy.
In addition to medical treatments, there are several lifestyle changes that can help individuals with muscular dystrophy manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. For example, maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can help improve muscle strength and prevent complications such as obesity and heart disease. It is also important for individuals with muscular dystrophy to get regular medical check-ups to monitor their symptoms and detect any potential complications early on.
Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder that affects muscle function and structure. While there is currently no cure for the disease, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. With ongoing research and advances in medical technology, there is hope that new treatments and even a cure may one day be available for individuals with muscular dystrophy.