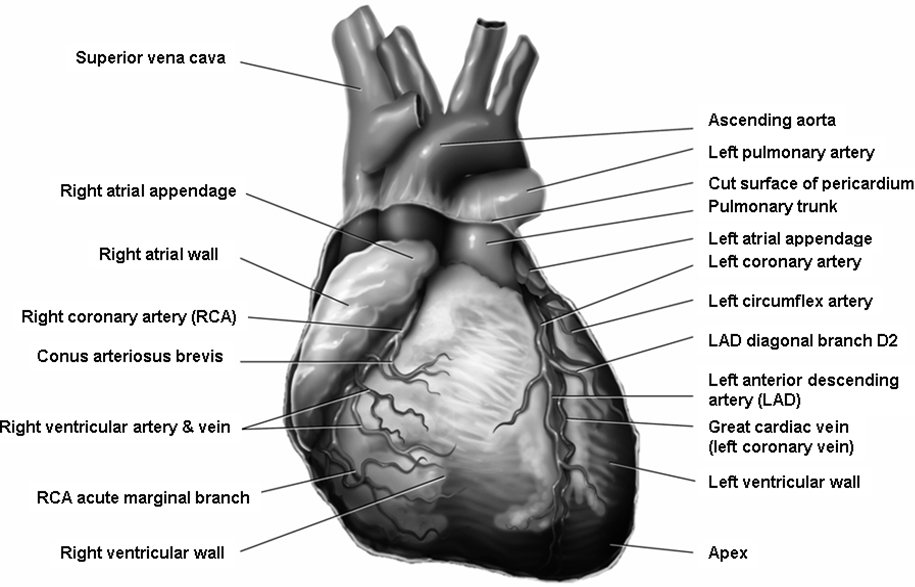
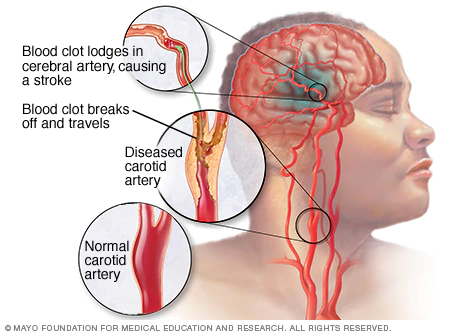
Hi friends , life is not a bed of roses and lilies . One must burn midnight oil to make it healthier and happier . To be in a healthier comfort zone there are some important things to remember.
Physical activity is an essential component of basic health care measures. Taking interest in regular exercise can help prevent chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. It is recommended that adults get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. This can be achieved through activities such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. Additionally, strength training exercises can help improve muscle mass and bone density, reducing the risk of injury and falls.
A healthy diet is another critical aspect of basic health care. Eating a balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases. It is also important to limit processed and high-fat foods, as well as sugary drinks and snacks. Making small changes in your daily routine, such as choosing to snack on fresh fruit instead of chips, can have a big impact on your overall health.
Sleep is crucial for physical and mental well-being. Lack of sleep can lead to a weakened immune system, increased stress levels, and a higher risk of chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Developing healthy sleep habits, such as sticking to a regular sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine, can help improve the quality of your sleep.
Stress can have a significant impact on your overall health, both physically and mentally. Chronic stress can increase the risk of conditions such as anxiety, depression, and heart disease. Adopting stress-management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and improve overall well-being. Additionally, engaging in activities that you enjoy, such as reading or spending time with friends, can also help reduce stress.
Incorporating these basic health care measures into your daily routine can help improve your overall health and reduce the risk of chronic conditions. Making small changes, such as going for a daily walk or choosing healthier snacks, can have a big impact on your physical and mental well-being. Remember, taking care of your health is a long journey and small steps taken consistently can lead to significant improvements over time. Stay blessed